As long as I can remember I’ve always had an interest for investing. Maybe it stems from my “lawn mowing” days in high school where I learned firsthand working for myself and making my own money was the way to go.
I loved working on my own schedule and not someone else’s. One of the things I realized while living at home with minimal expenses was how quickly money was coming in mowing yards yet sitting dormant in a checking account.
This inspired me to educate myself about how to get my money working for me which led me to Vanguard mutual funds.
Not only do they have a large selection of funds but their extremely low expense ratios make them one of the most popular mutual fund companies in the world.
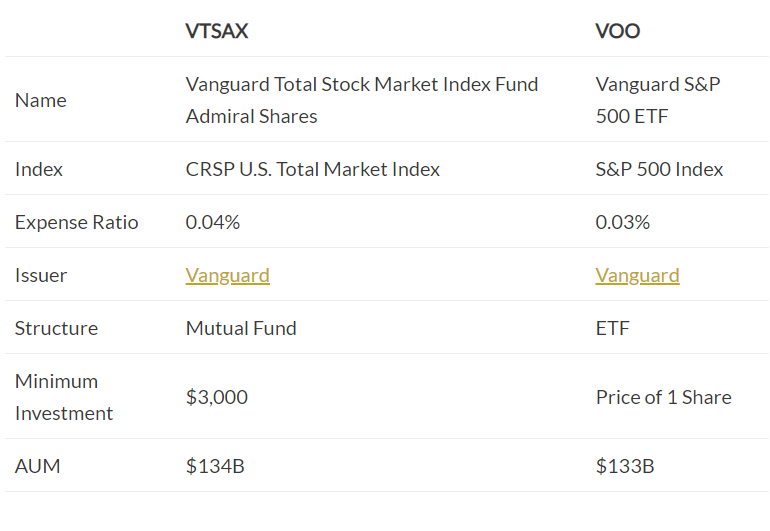
In this article, we’re going to take a look at two of Vanguard’s funds: VTSAX vs. VOO
Don’t Miss Any Updates. Each week I’ll send you advice on how to reach financial independence with passive income from real estate.
Sign up for my newsletterWhat Is An Index Fund?
If you’ve read any of my articles, you know that I’m all about investing passively in assets that will eventually lead to financial freedom. Even though most of our money each month goes toward real estate syndications, we do fund the practice’s retirement plan which consists mainly of index funds.
Index funds are extremely passive requiring little time or oversight vs someone that invests in individual stocks.
They allow you to invest in hundreds (sometimes thousands) of stocks at once which helps lower risk vs investing in one or two stocks.
According in Investopedia: An index fund is a type of mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) with a portfolio constructed to match or track the components of a financial market index, such as the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index (S&P 500). An index mutual fund is said to provide broad market exposure, low operating expenses, and low portfolio turnover. These funds follow their benchmark index regardless of the state of the markets.
These funds are typically purchased through platforms such as:
- Vanguard
- Fidelity
- Merrill Lynch
- Charles Schwab
Vanguard History
Because we’re going to discuss two of Vanguard’s more popular funds, let’s take a brief look of how they were started.
The late Jack Bogle founded Vanguard in 1975. What makes Vanguard so unique is that its investors are the owners. Because of this structure, they’re able to reinvest profits and keep costs ultra low.
Today there are websites and forums of loyal “Bogleheads” that continue to follow his low cost, index fund investing principles.
In 1976, Bogle was credited as starting the first index fund, the Vanguard 500 Index Fund (VFINX).
Back then, the common investment practice was either buying individual stocks or hiring an advisor to manage your portfolio. Bogle created quite a ruckus as he was looked upon as someone that conceded to match the market instead of trying to beat it.
If you know anything about Bogle then you know he was truly a visionary. He understood that simple indexing could outperform active management by a fund manager. This eventually led to his tremendous success in the investing world.
VOO vs. VTSAX – Overview
This article is going to compare two of Vanguard’s most popular funds: VTSAX vs VOO.
We’re going to break down some of the key differences including their:
- structure
- expense ratio
- minimum investments
We’ll also compare some of the risk metrics related to volatility and maximum drawdowns of each fund.
What is VTSAX?
VTSAX stands for Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund Admiral Shares that was created in 1992. It gives its investors exposure to the entire US stock market, including small, mid, and large-cap growth and value stocks.
It’s the world’s largest fund and known for its:
- low costs
- broad diversification
- potential for tax efficiency
Portfolio Composition
VTSAX’s top sectors include technology, financials, consumer services, industrials, and healthcare.
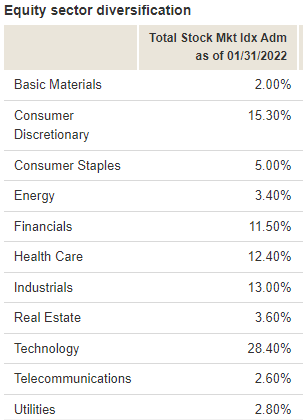
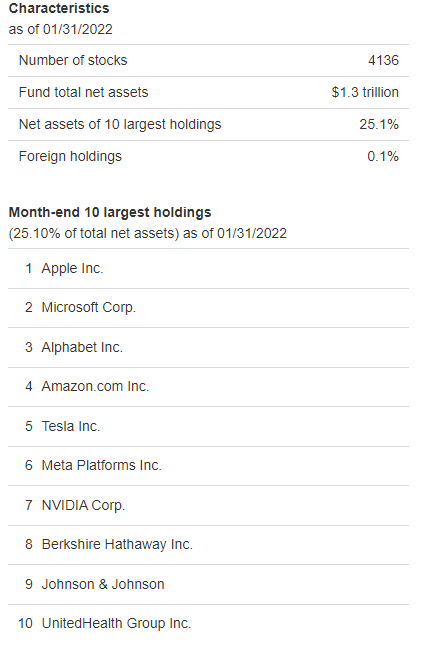
VTSAX Holdings
The number of holdings for VTSAX is just over 4,000 stocks. It seeks to emulate the performance of the entire U.S. stock market.
What is VOO?
The Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) has a more narrower focus compared to VTSAX.
VOO tracks the S&P 500, which is comprised of the 500 largest companies in the United States and is considered a gauge of overall U.S. stock returns.
Portfolio Composition
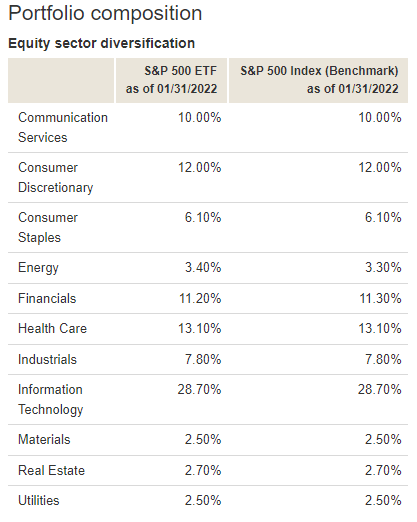
VOO Holdings
The number of holdings for VTSAX is just over 500 stocks. It seeks to emulate the performance of the S&P 500.
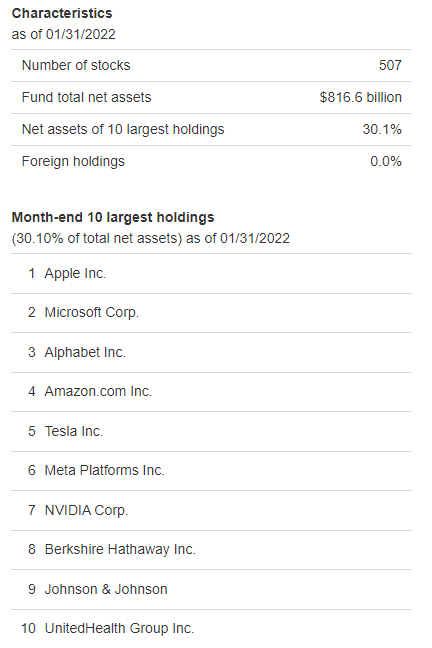
VOO vs VTSAX – What’s The Difference?
VTSAX vs VOO Performance
At first glance of both of the fund’s holdings, you’d think that they are they same but VOO and VTSAX are not the same funds as they each track different indexes.
But they are very similar in their performance.
Here’s how their performance compares over the last 10 years:
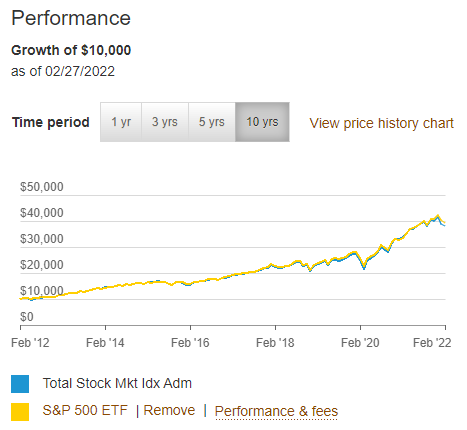
As you can see from the chart, their performance is almost identical with VOO slightly outperforming.
Fund Type
VTSAX is a total US stock market fund whereas VOO is a S&P 500 fund.
A total stock market fund provides slightly more diversification but slightly more risk. This is due to them holding smaller and mid-sized companies.
They’re generally viewed as riskier because they have more opportunity to grow, but also have a higher likelihood of failing.
VOO attempts to match the S&P 500 index set by Standard and Poor’s. It simply carries the biggest 500 companies in the United States.
Despite these slight differences, It’s worth noting that Vanguard rates both funds at the same risk level and both have provided very similar returns over the past 5 years.
ETF vs Index Fund
VTSAX is an index fund whereas VOO is an exchange traded fund (ETF). Typically ETFs are the more accessible option for new investors since they don’t have a minimum investment.
ETFs are also available to trade at anytime the market is open vs index funds are bought after the market closes.
For long-term investors, the ability to trade anytime during the day shouldn’t make much of a difference.
ETFs must be purchased one full share at a time which can occasionally lead to money left not invested. But index funds offer fractional share buying which allows you to invest the total amount you want at that time.
Minimum Initial Investment
VTSAX has a $3,000 minimum investment whereas VOO doesn’t have a minimum (it’s the price of one share).
Over the long term, this difference does not matter either.
VTSAX vs VOO – Why Simple Matters
The good news is that you can’t go wrong with choosing between VTSAX vs VOO as they’re both so similar.
Both funds are NOT actively managed as they match a broad, underlying index. Also, their expense ratios and costs are extremely low compared to other major funds.
One of John Bogle’s investment strategies is keeping things simple by investing in passively managed funds such as the Three Fund Portfolio.
Related article: The Vanguard Three Fund Portfolio
This strategy consists of putting together a three fund investment portfolio that invest in the following asset classes:
- US Stocks
- US Bonds
- International Stocks
The goal is to build a diversified portfolio as easily as possible.
For the US Stocks fund, you could choose between VOO or VTSAX.
In this article we’ve looked at several factors between VTSAX and VOO.
Overall, you can’t go wrong with either fund. If you prefer a little more exposure to small-cap securities then VTSAX is for you.
If you’d rather place your trust in America’s top 500 companies then VOO would be your choice.
Join the Passive Investors Circle